PCOD-PCOS
What Is PCOS ?
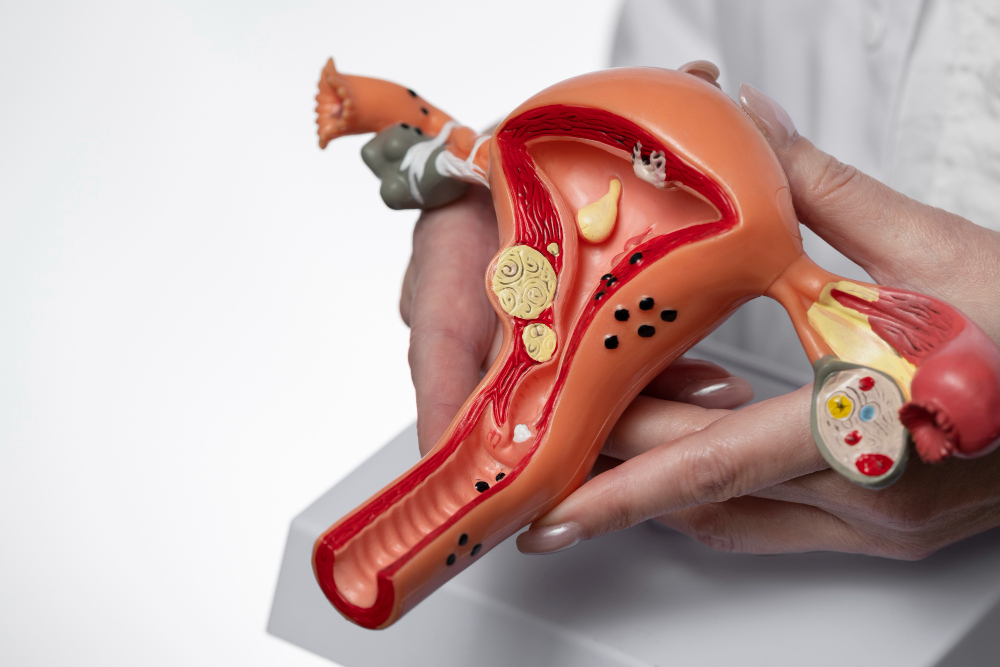
In each menstrual cycle, follicles grow on the ovaries. Eggs develop within those follicles, one of which will reach maturity faster than the others and be released into the fallopian tubes. This is "ovulation". The remaining follicles will degenerate.In the case of polycystic ovaries, however, the ovaries are larger than normal, and there are a series of undeveloped follicles that appear in clumps, somewhat like a bunch of grapes. Polycystic ovaries are not especially troublesome and may not even affect your fertility.
However, when the cysts cause a hormonal imbalance, a pattern of symptoms may develop. This pattern of symptoms is called a syndrome. These symptoms are the difference between suffering from polycystic ovary syndrome and from polycystic ovaries.So you can have polycystic ovaries without having PCOS. However, nearly all women with PCOS will have polycystic ovaries. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is the name given to a metabolic condition in which a woman will have polycystic ovaries, along with a certain pattern of other symptoms that reflect imbalances in reproductive and other hormones.
PCOS AND ACNE ?
Acne is a common symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome. It is an inflammatory skin disorder that involves interactions between hormones, hair, sebaceous (oil-secreting) glands and bacteria. Women with PCOS are susceptible, possibly due in part to excess levels of androgens (male sex hormones) in the skin. Teenagers are also susceptible around the onset of puberty due to an increase in the production of androgens. This androgen, a metabolite of testosterone, is called DHT.
It is thought that DHT stimulates the production of oil, which eventually can lead to clogged glands or pores. Clogged pores can no longer release oil and allow bacteria to grow and multiply in the follicle, leading to inflammation. Enzymes from this bacteria breakdown triglycerides in the sebum (oil) to form "free fatty acids" that further irritate the follicular wall. Rupture of the follicle, accompanied by the release of free fatty acids, bacterial products and keratin, results in an abscess that heals with scars in severe cases.
Treatment Options For Acne ?
Oral or topical tretinoin or isotretinoin. Oral tretinoin should only be prescribed by a physician who thoroughly understands its adverse effects. Pregnancy testing is important prior to beginning tretinoin therapy and at monthly intervals, due to the risk of severe fetal abnormalities that can occur if pregnancy results while taking this drug. Its acts by unplugging acne follicles and bringing acne pimples (comedones) to the surface. This is why tretinoin makes acne look worse in the first few weeks of treatment. Over-the-counter topical preparations containing benzoyl peroxide, which is an anti-bacterial agent. Over-the-counter topical preparations containing sulfur, which is a keratolytic (peeling agent) and also helps suppress the growth of bacteria. Topical agents containing azelaic acid. Azelaic acid exerts an antibacterial effect. It is also keratolytic and has a therapeutically positive effect on the formation of comedones (blackheads, whiteheads). In severe cases, the antibiotics tetracycline or minocycline may be used. Antibiotics are anti-bacterial agents. Increased exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet light (such as tanning beds). The ClearLight system, which uses a narrow-band, high-intensity light known as blue light to attack the bacteria in pimples. Available from some dermatologists. In the case of women with PCOS and acne, physicians will typically prescribe spironolactone and birth control pills. Some birth control pills contain lower levels of androgens and should, at least theoretically, provide better acne control.
Avoid using drugs that may cause acne. Avoid exposure to oil or grease. Use hypoallergenic cosmetics and soaps if available. Wash the affected areas thoroughly twice daily, or more if needed, to remove excess oils. Wash pillowcases and sheets regularly in chemical-free (no added colors or fragrances) detergents. Get adequate sun exposure.
Clinical Services
Facilities
24 Hours Services



